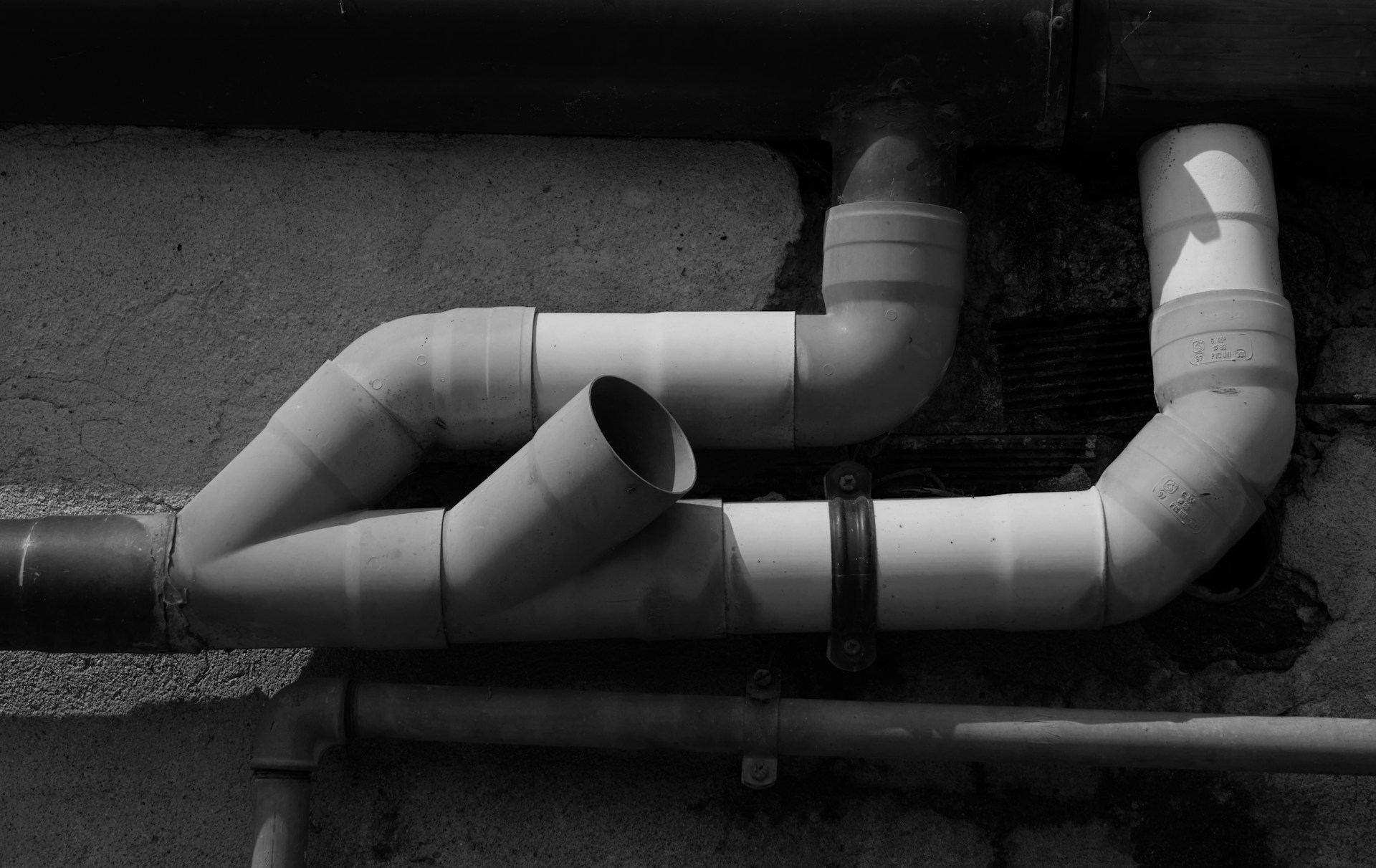
Property owners facing sewer line issues often wonder about their repair options, particularly whether modern trenchless methods can work with their existing pipes. The technology has revolutionized the industry by eliminating the need for extensive excavation, but understanding pipe compatibility remains crucial for successful project outcomes.
Trenchless technology offers significant advantages over traditional excavation methods, including reduced property damage, faster completion times, and lower overall costs. However, the effectiveness of these innovative sewer solutions depends heavily on various factors, including pipe material, condition, and configuration. Before committing to trenchless applications, homeowners and commercial property managers need comprehensive information about what makes their pipes suitable candidates for these advanced repair methods.
The compatibility question affects both the feasibility and long-term success of trenchless repairs. While these methods work exceptionally well in many situations, certain pipe characteristics can limit their effectiveness or make traditional excavation a better choice. Understanding these limitations helps property owners make informed decisions about their sewer repair investments.
Understanding Trenchless Technology Types
Cured-in-Place Pipe (CIPP) Lining
CIPP represents one of the most versatile trenchless rehabilitation methods available today. This process involves inserting a resin-saturated liner into the existing pipe, then curing it to form a new pipe within the old one. The method works effectively with various pipe materials and can navigate bends and joints with relative ease.
The process begins with thorough pipe cleaning and inspection using advanced camera technology. Once prepared, technicians insert the liner using air or water inversion, ensuring complete coverage of the damaged sections. The curing process, typically accomplished through hot water or steam, transforms the flexible liner into a rigid, durable pipe that can last decades.
Pipe Bursting Technology
Pipe bursting offers a complete replacement solution that breaks apart the existing pipe while simultaneously installing new high-density polyethylene (HDPE) material. This method requires two access points but eliminates the old pipe, making it ideal for severely damaged lines that cannot support lining methods.
The bursting head breaks the old pipe into fragments while pulling the new pipe into place. HDPE pipes used in this process feature heat-welded seams, creating continuous lines with minimal connection points. This results in stronger, more durable replacements that resist root intrusion and corrosion better than traditional materials.
Pipe Pulling Methods
Pipe pulling techniques work by attaching new pipes to existing ones and drawing them through the same route during the removal of the old system. This approach proves particularly effective for water line replacements where maintaining the exact pipe path is essential for proper system function.
Material Compatibility Analysis
Clay Pipe Systems
Clay pipes, common in older installations, present unique challenges for trenchless applications. These materials often suffer from root intrusion, joint separation, and structural deterioration that can complicate repair efforts. CIPP lining works well when clay pipes maintain structural integrity, but severely damaged sections may require pipe bursting or traditional replacement.
The age and condition of clay systems significantly impact compatibility decisions. Pipes installed before modern joint sealing techniques may have numerous entry points for roots and debris. Thorough camera inspection reveals whether existing clay lines can support trenchless rehabilitation or require complete replacement.
Cast Iron Considerations
Cast iron pipes, prevalent in mid-20th-century construction, often experience internal corrosion and scale buildup that affects trenchless compatibility. The material’s tendency to develop tuberculation can create irregular internal surfaces that complicate lining installation and reduce effectiveness.
Successful trenchless repair of cast iron systems typically requires extensive cleaning before liner installation. High-pressure water jetting or mechanical cleaning removes scale deposits and prepares surfaces for proper liner adhesion. However, severely corroded cast iron may need complete replacement through pipe bursting methods.
PVC and Modern Plastic Pipes
Modern plastic pipes generally offer excellent compatibility with trenchless methods. PVC systems maintain smooth internal surfaces and resist corrosion, making them ideal candidates for CIPP lining when structural damage occurs. The material’s flexibility also accommodates thermal expansion during the curing process.
Plastic pipe failures typically result from ground movement, improper installation, or external damage rather than material degradation. These specific failure modes often respond well to targeted trenchless repairs that address localized problems without affecting the entire system.
Pipe Condition Assessment Factors
Structural Integrity Requirements
The structural condition of existing pipes directly impacts trenchless method selection and success rates. Pipes with maintained structural integrity can support CIPP lining, while systems with significant collapse or deformation may require pipe bursting or traditional replacement methods.
Professional assessment involves a comprehensive camera inspection to evaluate pipe walls, joint conditions, and overall structural stability. This evaluation identifies sections that can support rehabilitation versus areas requiring complete replacement. The assessment also reveals root intrusion, debris accumulation, and other factors affecting repair success.
Diameter and Configuration Limitations
Pipe diameter significantly influences the applicability of the trenchless method. CIPP lining reduces internal diameter slightly, which may affect flow capacity in smaller pipes. Pipes below certain diameter thresholds may not accommodate lining materials effectively, requiring alternative repair approaches.
Complex pipe configurations, including sharp bends, multiple connections, and varying elevations, can complicate trenchless installations. While modern equipment handles most standard configurations, extreme angles or numerous service connections may necessitate partial excavation or alternative repair strategies.
Root Intrusion Impact
Root intrusion presents one of the most common compatibility challenges for trenchless repairs. Heavy root presence can prevent proper liner installation and compromise long-term repair effectiveness. Successful trenchless rehabilitation requires thorough root removal before liner installation.
The root removal process involves mechanical cutting or chemical treatment to clear pipe interiors completely. However, recurring root problems may indicate ongoing issues that trenchless methods cannot address permanently, making complete pipe replacement a more viable long-term solution.
Geographic and Environmental Considerations
Soil Conditions and Pipe Stability
Soil conditions significantly influence trenchless method success rates and long-term performance. Stable soils support pipe structures during rehabilitation, while shifting or unstable ground can compromise repair integrity. Clay soils, in particular, can create ongoing pressure that affects both existing pipes and trenchless repairs.
The evaluation process must consider soil composition, drainage characteristics, and seasonal movement patterns. Areas with high water tables or frequent freeze-thaw cycles may experience ongoing ground movement that affects pipe stability regardless of the repair method used.
Regional Climate Factors
Climate conditions affect both the trenchless repair process and long-term performance outcomes. Temperature extremes can influence curing times for CIPP installations and affect material performance over time. Regional precipitation patterns also impact soil stability and groundwater levels around pipe systems.
Cold climate installations require special consideration for curing processes and material selection. Hot water curing methods may need adjustment for extreme temperatures, while material choices must account for thermal expansion and contraction cycles throughout the year.
Access and Site Constraints
Physical site constraints often determine trenchless method feasibility regardless of pipe compatibility factors. Limited access to equipment, proximity to structures, and utility conflicts can restrict available repair options. Urban environments present particular challenges with space limitations and coordination requirements.
The assessment process must evaluate equipment access routes, staging areas, and potential conflicts with existing utilities or structures. These practical considerations often influence repair method selection as much as technical pipe compatibility factors.
Making Informed Repair Decisions
Understanding pipe compatibility with trenchless methods requires a comprehensive evaluation of multiple factors working together. Material type, structural condition, environmental factors, and site constraints all influence the success potential of different repair approaches. Professional assessment provides the detailed analysis needed for optimal repair method selection.
Property owners benefit most from consulting experienced trenchless specialists who can evaluate their specific situations comprehensively. Companies like Shaw Trenchless bring decades of combined experience to pipe compatibility assessments, ensuring repair methods match actual site conditions and performance requirements.
The investment in proper evaluation pays long-term dividends through improved repair success rates and extended system life. While trenchless methods offer significant advantages in appropriate applications, understanding their limitations ensures realistic expectations and optimal outcomes for sewer repair projects. Visit https://www.shawtrenchless.com/ now to learn more!