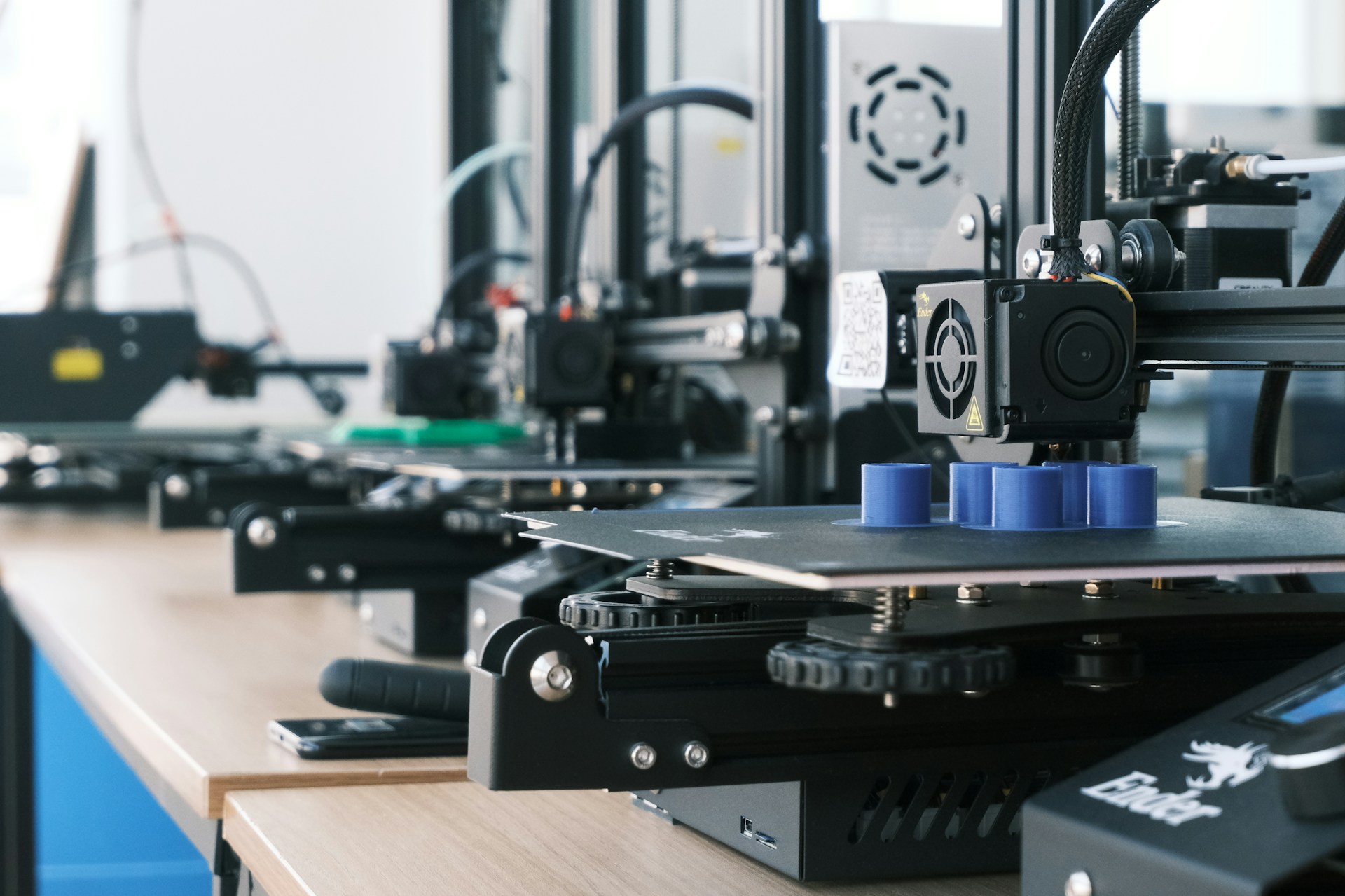
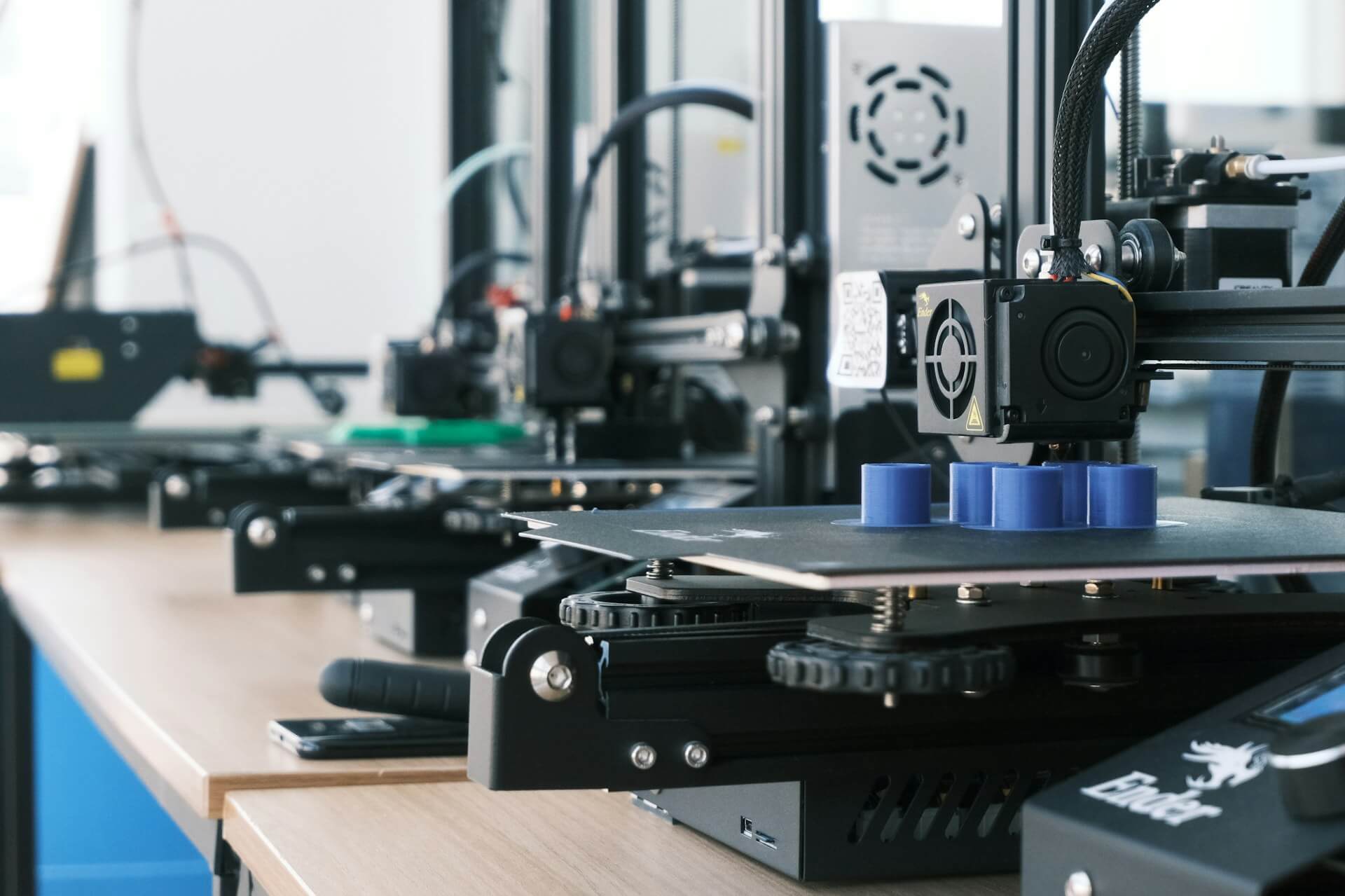
In recent years, the food manufacturing industry has witnessed a revolutionary transformation with the advent of 3D printing technology.
This innovative approach to food production has opened up exciting possibilities for creating unique, personalized, and nutritionally tailored food items.
As we delve into the prospects of 3D printing in food manufacturing, it’s essential to understand how this technology is reshaping the culinary landscape and what it means for consumers and businesses alike.
3D printed food, also known as additive manufacturing in the food industry, is rapidly gaining traction as a game-changing technology.
This website aims to explore the potential impact of 3D printing on the future of food production, highlighting its benefits, challenges, and the exciting opportunities it presents for both manufacturers and consumers.
The Rise of 3D Printing in Food Manufacturing
Revolutionizing Culinary Creation
3D printed food is no longer confined to the realm of science fiction. This groundbreaking technology is rapidly transforming the food industry, offering unprecedented precision and customization in food production.
By utilizing specialized printers, manufacturers can now create intricate three-dimensional food items layer by layer, following detailed digital designs.
Applications Across the Food Industry
The potential applications for 3D printed food are vast and varied:
- High-End Restaurants: Chefs are experimenting with unique textures and shapes, pushing the boundaries of culinary artistry.
- Large-Scale Manufacturers: Companies are exploring more efficient production methods, potentially revolutionizing mass food production.
- Personalized Nutrition: 3D printing technology enables the creation of customized meals tailored to individual dietary needs and preferences.
Addressing Industry Challenges
Beyond its creative applications, additive manufacturing in the food industry has the potential to tackle some of the sector’s most pressing issues:
- Sustainability: By optimizing ingredient use, 3D printing can significantly reduce food waste.
- Efficiency: The precision of 3D printing allows for more streamlined production processes.
- Innovation: This technology opens up new possibilities for food product development and customization.
As 3D printed food continues to evolve, it promises to reshape our relationship with food, from production to consumption, ushering in a new era of culinary innovation and efficiency.
Personalized Nutrition Solutions Through 3D Printing
The Future of Personalized Nutrition
3D printing is emerging as one of the most innovative food production techniques, offering unprecedented opportunities for personalized nutrition solutions.
This groundbreaking technology allows for the creation of food items tailored to individual dietary needs, nutritional requirements, and taste preferences.
Benefits of 3D-Printed Personalized Nutrition:
• Precision Nutrient Composition: Create meals with exact nutritional profiles
• Customized Dietary Management: Easily cater to specific health conditions or restrictions
• Enhanced Healthcare Nutrition: Improve patient care with tailored hospital meals
• Athletic Performance Optimization: Design meals to support specific training regimens
By harnessing the power of 3D printing, we’re not just changing how food is made—we’re transforming how nutrition is delivered and consumed. This technology promises to make maintaining a balanced diet more accessible and effective than ever before.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction in Food Production
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is revolutionizing the food industry with its innovative food production techniques. This technology offers significant advantages in terms of sustainability and waste reduction:
- On-Demand Production: 3D printing enables manufacturers to produce food items as needed, reducing overproduction and storage requirements.
- Ingredient Efficiency: The precision of additive manufacturing leads to more efficient use of ingredients, minimizing waste during production.
- Alternative Ingredients: 3D printing facilitates the use of sustainable alternatives, such as plant-based proteins and insect-based ingredients.
- Resource Conservation: By optimizing ingredient use and reducing waste, 3D printing contributes to more sustainable resource management in food production.
These benefits make additive manufacturing a promising solution for addressing sustainability challenges in the food industry, paving the way for more environmentally friendly food production practices.
Enhancing Food Safety and Traceability
3D printed food technology is revolutionizing the food manufacturing industry, offering unprecedented advantages in food safety and traceability. This innovative approach to food production provides:
- Controlled Environment: 3D printing significantly reduces contamination risks, leading to safer food products.
- Digital Traceability: Every production step is digitally recorded, enhancing transparency and facilitating efficient recall processes.
- On-Demand Freshness: 3D printed food can be produced just in time, potentially reducing the need for preservatives and aligning with the growing demand for cleaner labels.
Moreover, 3D printed food opens the door to personalized nutrition solutions, allowing for precise control over ingredients and portion sizes.
This technology empowers consumers to make informed dietary choices while giving manufacturers the tools to meet diverse nutritional needs efficiently and safely.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printed Food
While additive manufacturing in food production offers exciting possibilities, it’s crucial to understand its current limitations:
Ingredient Constraints
- Limited Range: 3D food printers can only work with specific ingredients, restricting texture and consistency options.
- Texture Challenges: Replicating complex food textures remains a significant hurdle in these innovative food production techniques.
Production Speed
- Time-Intensive Process: Current 3D food printing is slow, making large-scale production impractical.
- Efficiency Improvements Needed: Advancements in technology are essential to overcome these speed limitations.
Regulatory Hurdles
- Safety Standards: New guidelines for assessing 3D printed food safety and nutritional value are necessary.
- Quality Control: Regulatory bodies must develop protocols specific to this novel food production method.
Consumer Acceptance
- Education Required: Informing the public about 3D printed food benefits and safety is crucial for widespread adoption.
- Overcoming Hesitation: Some consumers may be reluctant to embrace this unconventional approach to food manufacturing.
As the technology evolves, these challenges in additive manufacturing for food production are likely to be addressed, paving the way for more widespread implementation of this innovative technique.
The Future of Culinary Creativity and Innovation
Revolutionizing Food Production and Consumption
3D printing technology is poised to transform the landscape of food manufacturing, ushering in a new era of innovative food production techniques.
This groundbreaking approach offers unprecedented opportunities for culinary creativity and personalized nutrition solutions. By leveraging 3D printing, chefs and food manufacturers can:
• Create intricate designs and textures previously unattainable
• Develop unique flavor combinations tailored to individual preferences
• Produce visually stunning, plant-based alternatives that closely mimic traditional meat products
Addressing Global Challenges
Beyond its applications in gourmet cuisine, 3D food printing has the potential to tackle pressing global issues:
• Food Security: By enabling the production of nutritious food from sustainable ingredients, this technology could provide solutions for areas facing scarcity.
• Personalized Nutrition: 3D printing allows for the creation of meals precisely tailored to individual nutritional needs, opening new avenues for health-conscious consumers and those with dietary restrictions.
As we look to the future, 3D printing in food manufacturing stands at the forefront of culinary innovation, promising to revolutionize not just how we produce food, but how we think about and experience it.
Conclusion
As we look to the future, it’s clear that 3D printing has the potential to impact the food manufacturing industry.
From personalized nutrition solutions to more sustainable production methods, these innovative food production techniques are set to reshape how we produce, consume, and think about food.
While there are still challenges to overcome, the prospects of 3D printing in food manufacturing are undeniably exciting.
As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see more widespread adoption across the food industry, leading to innovations, sustainability, and culinary creativity.
Whether you’re a food manufacturer looking to explore new production methods, a chef seeking to push the boundaries of culinary creativity, or simply a food enthusiast curious about the future of nutrition, the world of 3D printed food offers exciting possibilities.